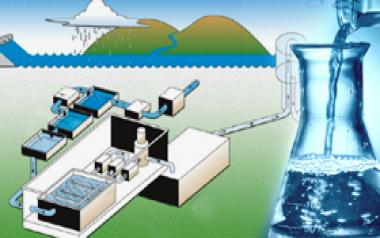
Water Treatment Process: An Overview
Treatment for drinking water production involves the removal of contaminants from raw water to produce water that is pure enough for human consumption without any short term or long term risk of any adverse health effect. Substances that are removed during the process of drinking water treatment include suspended solids, bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi, and minerals such as iron and manganese.
The processes involved in removing the contaminants include physical processes such as settling and filtration, chemical processes such as disinfection and coagulation and biological processes such as slow sand filtration.
Measures taken to ensure water quality not only relate to the treatment of the water, but to its conveyance and distribution after treatment. It is therefore a common practice to keep residual disinfectants in the treated water to kill bacteriological contamination during distribution.
JICA Assisted 191 Million Litre Per Day Kharghuli Water Treatment Process
- Raw water is pumped from Intake Well to Pre Settling Tank(PST)through 1300MM diameter MS pipe line.
- Raw water entering into PST will be allowed first settlement sludge in PST.
- Semi cleared water will be entering into Cascade Aerator, where aeration will be take place.
- Flash Mixer: - Here the aerated water will be added with chemicals like Polyelectrolyte, aluminum sulphate, lime and pre-chlorine using flash mixer.
- Chemical added water will be retained in flocculators so to allow the sludge to settle down.
- Water from flocculator will be allowed to enter in to tube settler, where further settlement of sludge will take place.
- Water from tube settlers will be allowed to pass through the filter beds, where water gets 100% cleared.
- Clear Water from Filter will enter in to Clear Water Reservoir, where post Chlorine will be added.
- This treated water will be pumped through 1500 mm diameter MS pipe line to Ramsa hill reservoir from where water by gravity will move to other reservoirs